2020. 2. 8. 22:21ㆍ카테고리 없음
The Periodic Trend. Due to each atom’s unique ability to lose or gain an electron, periodic trends in ionic radii are not as ubiquitous as trends in atomic radii across the periodic table. Periodic(Trends(Worksheet(((Answer Key 1. Circle)the)element)withthe)largest)atomic)radius)andput)a)square)aroundthe)element)withthe)smallest) atomic)radius:))) Cu) K) Ni) Br))) Largest – K Smallest - Br) Explainwhy)you)madethesechoices.) Atomic radius decreases as you go left to right across a period. Potassium is in the far. Interactive periodic table with element scarcity (SRI), discovery dates, melting and boiling points, group, block and period information.
The first periodic table was created by Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian professor in 1869. Taking his name, it was named the Mendeleev periodic table, in which the chemical elements are positioned in order of their increasing mass number. In the history of periodic table, lots of changes were being made with the discovery of elements and theoretical assumptions. Finally, the modern, labeled periodic table of elements with names is developed for reference of chemical elements at a glance. The modern periodic table has a lot to say about the chemical elements, besides the atomic number, atomic weight, and symbol of the identified elements.
For example, chemical elements falling in the same group share common properties, which are different from other groups. Also, go through the periodic table trends and you will come to know a regular pattern in the alteration of physical and chemical properties of elements, as you go from left to right, from top to down direction, and vice versa. Trends in the Periodic Table of Elements In chemistry, understanding the basic periodic table facts is like learning the A, B, C. Of the English language. In fact, this tabular representation of elements is the base for chemistry subject.
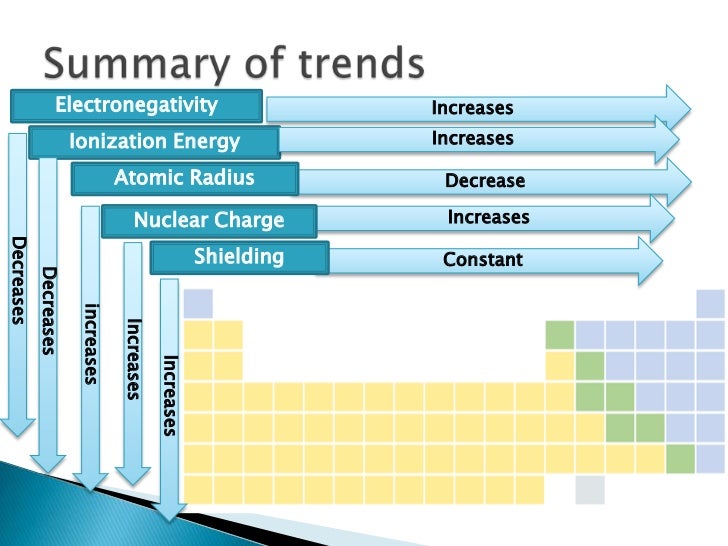
Refer to the arrangement of elements in the periodic table; the horizontal row of element is called period and the same in vertical column is called group. Detailed information regarding trends in the modern periodic table is highlighted below. Atomic Radius Trend Consider two atoms of the same element that touch each other by their outer edges. Measure distance between the centers of the two adjacent atoms and half of the value is called atomic radius of the element. The atomic radii of elements gradually increases as you move across (from right to left) in a period, and down (from top to bottom) in a group.
Ionic Radius Trend Similar to the atomic radius, the radii of positive ions (cations) and negative ions (anions) of chemical elements can be measured. When a comparison is made between the two ionic forms of a same element, it is found that the positive charged ion has a smaller radius than the radius of the negatively charged ion. Ionization Energy Trend The ionization energy of an element is defined as the total energy required to remove an electron from an atom (when it is in the neutral state). After detaching the electron, the same atom turns into positive ion. Coming to periodic table trends regarding this, the first ionization energy goes higher from left to right direction, while it drops from top to bottom direction. Electron Affinity Trend In contrary to ionization energy, the electron affinity is defined as the change in the energy state, when an extra electron is introduced into an atom (when it is in the neutral state). After adding electron, the same atom becomes a negative ion.
The electron affinity of elements increases from left to right in a period, and from bottom to top in a group. Electronegativity Trend When one or more electrons are shared between two atoms, each atom has a tendency to attract the electrons towards it. The measure of this value is called electronegativity. The electronegativity of elements increases as you move from left to right direction in the periodic table, and the same decreases while moving from the top to bottom direction.
Metallic Property Trend As per chemistry discipline, each of the chemical elements possesses metallic property, which is measured in terms of low to high scale. When this attribute is linked to trends in the periodic table, the metallic property of elements drops with increasing atomic number in a period, while it increases with increasing atomic number in a group. Lattice Energy Trend Lattice energy is the amount of energy released, when two oppositely charged ions of the same element in gaseous state fuses to form a solid.
The lattice energy increases from top to bottom direction in a group. Also, this energy level is found to be elevated with respect to increase in the charge of the combining ions.
It is to be borne in mind that the above-mentioned trends in the periodic table do have exceptions for some elements or ionic forms. Also, as per the objective of your study, you can refer to several modified versions of the typical periodic table. You can either concentrate on the periodic table with atomic mass or periodic table with charges for precise information.
Periodic Trends 1. Atomic Radius Horizontal: The atomic radius of an element decreases from left to right within each period on the periodic table. Explanation: In understanding this trend, one must consider the charge and energy of the valance electrons.
As you move from left to right on the periodic table, the number of protons increases in increments of one. In addition to this, the number of electrons also increases by increments of one. These electrons are added to the same energy level (or ring). Therefore, the increased attraction of the nucleus pulls the electron closer to the nucleus, so the atom becomes smaller. Vertical: The atomic radius increases within a group as you descend the periodic table. Explanation: The atomic radius increases descending down a group of elements on the periodic table. Therefore, each row on the table contains one more energy level (or ring) than the previous row.
The farther an energy level is from the nucleus, the less attraction force is exerted on the electrons in the energy level. Also, the more rings an atom has, cause a greater amount of shielding, since each ring contributes to a greater shielding effect. First Ionization Energy Horizontal: As the atomic number of elements in the periodic table increases from left to right, the first ionization energy also increases from left to right. This means that the elements of Group 1 (alkali metals) have the lowest first ionization energy, and Group 18 elements (noble gases) have the highest first ionization energy. Explanation: When moving from left to right, the first ionization energy generally increases. This is due to the decreased atomic radius coupled with the increased effective nucleus charge. As a result, the force of attraction between the nucleus and outer most electrons increases, which leads to an increase in the amount of energy required to move an electron from the atom ( i.e., an increase in the first ionization energy).
Vertical: First Ionization energy decreases as you descend down the periodic table. Explanation: Ionization energy decreases as you as you move down a family or group in the periodic table because the valence electrons of the elements are in orbits that are farther from the nucleus. As the distance from the nucleus increases, the attraction of the electrons to the nucleus decreases, even though the size of the nuclear charge increases. Thus less energy is required to remove an electron from an atom further down a group.
(i.e., the ionization energy decreases down a group). The Group that has the 2nd highest ionization energy is the Halogen group. This is due to the fact that the atomic radius of the elements decrease as you move from right to left on the periodic table, And smaller the atomic radius is, the greater the amount of ionization energy is required. The Halogen group is second to the right of the periodic table, and thus has the 2nd highest ionization energy. Electron Affinity Horizontal: The electron affinity for an element increases as you move from left to right across the periodic table. Explanation: As you move from left to right across the periodic table, the number of valence electrons increases and the atomic radius decreases.
The force of attraction between the nucleus and valence electron increases, so more energy is released when a new electron is acquired. Vertical: The electron affinity decreases as you move down a group within the periodic table. Explanation: As you descend the periodic table in a given group the atomic radius increases therefor the force of attraction between the valence electron and the nucleus of the atom decrease. This leads to a decreasing electron affinity within a group as you move down the periodic table.

Follow-up Practice Questions: 1. Smallest radius to largest radius: O (oxygen), Sb (antimony), Sn (tin), Ba (barium), Cs (cesium). The periodic table organizes the elements according to general patterns of similarity. Below is a very small image of the periodic table. It is basically unreadable in terms of specific information, but it allows us to easily look at the periodic tables structure general trends.
Figure%: A very small periodic table The vertical columns of the periodic table (marked by yellow stripes in the figure) are called groups. The horizontal rows are called periods. There are 18 groups and 7 periods Words 754 - Pages 4. Activity, you are going to discover some of the trends of the properties that exist on the modern periodic table. To do this, you are going to graph these properties.
OBJECTIVES: The student will be able to define some of the properties of the element graph the properties of the elements (use Z = 1 through Z = 36 only) determine the general trends found on the periodic table PROCEDURE: 1. On your calculator or in Excel, graph the trend of density. The graph should have the atomic number Words 746 - Pages 3. To Trend or Not to Trend? Two decades ago Cesarean sections (C-sections) were only performed because of previous cesarean delivery, breech presentation, dystocia, fetal distress, and other emergencies (Tafel et al. 957), now commonly known as emergency C-sections. This widely considered timely operation might have caused the rate of women undergoing C-sections to increase (Beydoun, 334).
Since 1965, national U.S. C-section rate rose from 4% to the current 32.8% (Martin et al. Along with Words 5104 - Pages 21. Periodic Table of the Elements Chapters 4 & 10 (31) Chapter 5 (32) Interactive periodic table Why is the Periodic Table important to me?.
The periodic table is the most useful tool to a chemist. You get to use it on every test.
It organizes lots of information about all the known elements. Pre-Periodic Table Chemistry. was a mess!!!. No organization of elements. Imagine going to a grocery store with no organization!!. Difficult to find information. Chemistry didn’t make sense Words 1646 - Pages 7.
TRENDS IN THE PERIODIC TABLE OBJECTIVES: as given MTERIAL/APPARATUS: as given PROCEDURE: Part One: Atomic Radii of Elements Graph of Atomic Radii of the First 20 Elements on the Periodic Table Graph of Ionization Energies of the First 20 Elements from the Periodic Table QUESTIONS/DISSCUSSIONS Part One: 1. What is the group name for the elements found at the peals of your graph? What is the group located on the periodic table.
The group name of the elements at the peaks is Alkali Metals. The Words 604 - Pages 3. Nucleus to the boundary of the surrounding cloud of electrons. B) State and explain the trends in atomic radius for a period and a group. Ans: The trend for atomic radius for a period, in this case period 2, the radius decreases, because the number of orbitals is steady, but the increasing number of protons pulling on the same number of increasing electrons makes a ‘tighter’ attraction.
Periodic Trends Ionization Energy
The trend for atomic radius in a group, in this case group 1, is that the radius increases, as one Words 455 - Pages 2. Ibrahim Bholat (3) Boyer 11/19/14 Period 6 Lab Station #5 I. Purpose The purpose of the lab is to show correlation of activity and trends. Data Tables III. Graph (On Separate Graph Paper) IV.
Calculations Percent Error: Approximate Value – Exact Value / Exact Value X 100 Approximate Value: 5.3 Exact Value: 5.91 5.3 – 5.91 / 5.91 X 100 = 1.13% V. Which Group 1 metal, lithium, sodium, or potassium is most active? Cite your evidence. Potassium is the most active because Words 659 - Pages 3.
3875243 Trends with Electron Configuration The electron configuration of an element dictates the element's properties in a chemical reaction. Elements' electron configurations vary regularly along the periodic table. When dealing with the atomic radius, the size decreases going across of the table and increase going down the table. Moving down the atom, electrons are added to the atom, but each time the number of shells increases. Thus the atomic radii will go on increasing.
Periodic Trends Atomic Radius
When moving across Words 308 - Pages 2.